Department Menu
Overview
More than one billion people in the world experience some form of disability. Our goal: To enable every individual to participate in all of life’s activities. Our tools: Innovative ideas, practical solutions and never-say-never attitudes.
In Pitt’s Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology, the challenge is always on.
Faculty researchers are at the forefront of developing national and international standards for assistive technologies. They push the limits to bring new devices to market, while students develop interdisciplinary skills and gain hands-on experience in state-of-the-art laboratories and through clinical rotations.
There’s a spirit of collaboration between engineers, scientists, counselors and researchers to improve the mobility and quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
Programs
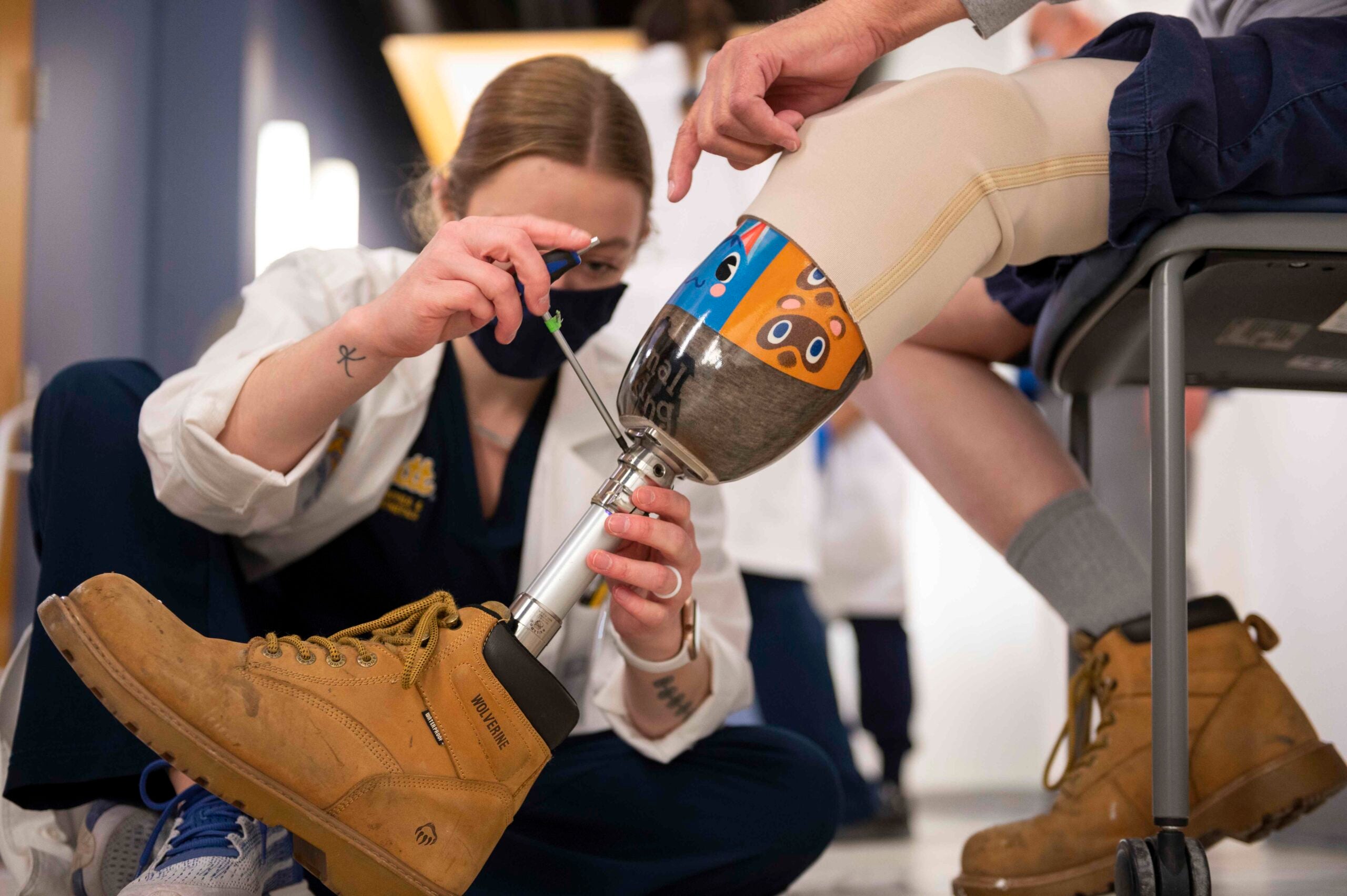

On-campus
Duration:
2 years,
(5 terms, including 1 summer term)
Program Start:
Fall term (August)
Application Closes: December 1, 2025
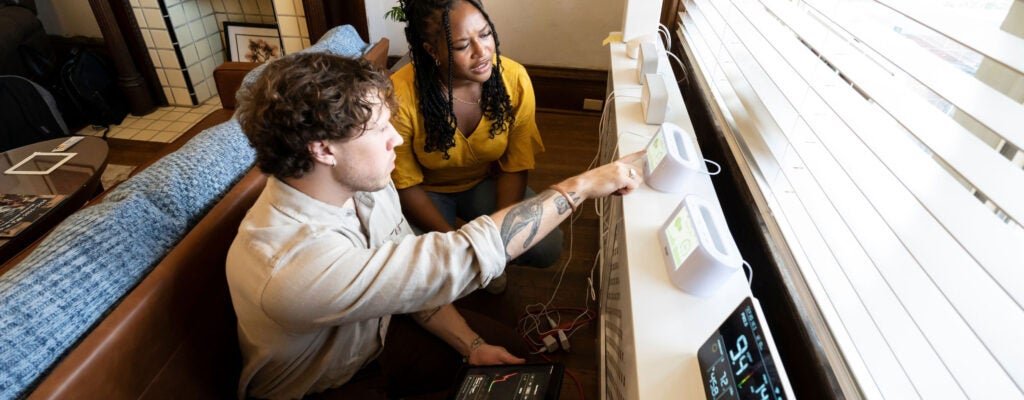

On-campus
Duration:
4-5 years
Program Start:
Fall term (August)
Application Closes: May 1, 2026
Hybrid
Duration:
Full-time
1 year
(3 terms, including 1 summer term)
Part-time
Varies and at the student’s pace
Program Start:
Fall term (August)
Application Closes: August 15, 2026
Scholarships
The Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology offers competitive fellowships to MS students and postdocs.
- View this scholarship page in late Fall of 2024 for possible scholarship opportunities for the 2025 school year.
- Student Research Opportunities
- AccelerATe
RST students are encouraged to apply for external funding. Below is a list of nationally competitive fellowships and funding databases. The links provide a basic summary of each fellowship. If you have specific questions regarding one of these fellowships, please contact the sponsor.
Available Scholarships
- A.T. Anderson Memorial Scholarship (Sponsor: American Indian Science & Engineering Society (AISES)
- Achievement Rewards for College Scientists Foundation (ARCS) Scholar
- American Association of University Women (AAUW)
- American Philosophical Society (APA) John Hope Franklin Dissertation Fellowship
- ASEE/ NSF Small Business Postdoctoral Research Diversity Fellowship
- Awards for African Americans, including Dissertation Research
- Cardiovascular Bioengineering Training Program (CBTP) (Funded by the NIH)
- College Scholarships, Graduate Fellowship & Postdoctoral Awards for Minorities
- Council for International Exchange of Scholars
- Developing Global Scientists and Engineers: International Research Experiences for Students (IRES) and Doctorial Dissertation Enhancement Projects (DDEP)
- Directorate for Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences (SBE) Doctorial Dissertation Research Grants
- Ford Foundation
- Foundation for Science & Disability
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute-Gilliam Fellowship
- Individual Advanced Research Opportunities Program (IARO)
- K. Leroy Irvis Fellowship
- National GEM Consortium
- National Hispanic Scholarship Fund
- National Institute of General Medical Sciences (Sponsored by NIH)
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Fellowships – Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards
- National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship (GRF)
- NSF fellowship
- NSPC Graduate Fellowship
- Research Associateship Programs (Sponsor: National Research Council (NRC) of the National Academies of Sciences
- Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards for Individual Predoctoral Fellowships to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research
- Scholarships4Development Database
- Soros Fellowships for New Americans
- The AAHD Frederick J. Krause Scholarship on Health and Disability – AAHD website.
- The Collegiate Inventors Competition (Sponsor: National Inventors Hall of Fame)
- The Hartwell Foundation
- The National Academies
- The Pittsburgh Foundation
- The Provost’s Office – University of Pittsburgh
- The Scott and Paul Pearsall Scholarship
- Training Grants – The Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition (CNBC)
- University of Pittsburgh, Office of Research
- Whitaker International Award For Bioengineers and Biomedical Engineers
- Woodrow Wilson Teaching Fellowships
AccelerATe
A diverse and well-trained workforce is critical to meet the needs of a growing number of individuals who can benefit from Assistive Technology (AT), a number expected to double from one to two billion people by 2050. To ensure that AT is appropriate for those who need it, the workforce must promote excellence in AT education, design, provision, manufacturing and research. To help fuel this workforce growth, the Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology (RST) is offering the AccelerATe Scholarship.
Scholars will receive a one-time maximum scholarship award of $5,000 (U.S.) to offset costs associated with RST degree-granting programs including the master’s in either Rehabilitation Technology (RT) or Prosthetics & Orthotics (P&O).
Eligibility
- Demonstrate financial need for the scholarship
- Be from a group that is under-represented in STEM or health care fields and/or have demonstrated leadership supporting disadvantaged groups, such as racial/ethnic minorities, sexual and gender minorities, individuals with disabilities, or those in low-resource settings.
How to Apply
Prospective students who submit an application to the Master of Rehabilitation Technology (MRT) and Prosthetics & Orthotics (P&O) programs will receive detailed information on how to apply for an AccelerATe Scholarship.
Application Requirements
- Financial Needs – In a few sentences, provide insight as to why you qualify for this scholarship based on financial need.
- Diversity and Inclusion – Submit an essay of no more than 400 words answering the following questions:
- How have you served as a role model for groups under-represented in STEM/health care?
- What activities did you participate in and how did your efforts support diversity and inclusion initiatives?
- How have your experiences and challenges related to diversity and inclusion shaped your career goals?
Selection of Awardees
Awardees will be selected by the RST Selection Committee.
Expectations of AccelerATe Scholars
- Maintain a good academic standing of at least a 3.0 GPA in your program and make continuous progress towards your degree.
- Participate in RST’s diversity and inclusion activities.
- Provide a half-page, written overview of your career goals and how the AccelerATe scholarship supported those goals following completion of your graduate degree program.
The AccelerATe Scholarship is sponsored by the Kaufman family.
Innovate, Educate, Elevate: Advanced Training in Rehabilitation Technology
A collaborative team of University of Pittsburgh faculty and external partners has been awarded a five-year, $875,000 training grant from the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services (OSERS). The grant, titled “Innovate, Educate, Elevate: Advanced Training in Rehabilitation Technology,” aims to expand the national workforce of highly skilled professionals delivering cutting-edge assistive technology (AT) services, with a focus on transition and vocational rehabilitation.
Over these five years, the initiative will:
- Fully fund 10 master’s students to become leaders in rehabilitation technology.
- Provide advanced training to 70 current professionals to strengthen national AT service capacity.
- Foster collaboration between academia, clinicians, educators, and policymakers to enhance accessibility and employment outcomes for individuals with disabilities.
The project officially launched on October 1, 2025
Training Opportunities
- Master’s in Rehabilitation Technology (MRT)
- Focus: Prepares students for clinical, research, and design careers in rehabilitation and nonprofit settings.
- Support: Full tuition, stipend, and professional development funding for 10 scholars (2 per year).
- See the program’s admissions page for more details.
- Continuing Education + ATP Certification Track
- Focus: Upskills professionals (rehabilitation counselors, OTs, PTs, special educators, technologists) working in vocational rehab or nonprofit settings.
- Support: Free access to online continuing education modules and waived RESNA Assistive Technology Professional (ATP) exam fee.
- Delivery: 100% online and asynchronous.
- Start Date: Flexible entry; ATP prep course offered in the fall semester.
- Size: Up to 14 participants per year (70 total).
- Eligibility: Current employment in a rehabilitation or nonprofit setting.

Master of Rehabilitation Technology Program Awarded $875,000 U.S. Department of Education Training Grant
The five-year grant will expand the national workforce of highly skilled professionals delivering cutting-edge assistive technology services, with a focus on transition and vocational rehabilitation.
Read the full storyResearch
In the Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology (RST), we engage in research of impact. Our research is focused on improving health and rehabilitation outcomes for people with disabilities through the integration of consumer experiences, engineering, assistive technology, medicine and clinical practice.
Research Areas
- Assistive Technology Innovation and Commercialization
- Solving user- and clinician-driven challenges by innovating and commercializing assistive technologies (ATs).
- Product Performance, Standards and Clinical Usability
- Conducting rigorous performance testing of assistive technologies, support surfaces, and seating systems to guide manufacturers, clinicians, and policymakers.
- Establishing national and international testing standards to ensure safety, effectiveness, and usability of mobility and rehabilitation technologies in real-world settings.
- Advancing solutions for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of soft tissue injuries through research on seating, support surfaces, and physiological factors that impact tissue viability.
- Smart Technology for Accessibility, Aging and Independence
- Advancing smart technology solutions—including wearables, smart home devices, and assistive robotics—to enhance accessibility, independence, and quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
- Using human-centered design to develop and evaluate smart technologies that support cognitive health, aging in place, and caregiving for individuals with neurodegenerative conditions.
- Supporting innovation and commercialization of assistive technologies, including clinical decision support systems and solutions that help older adults remain independent.
- Mobility, Prosthetics and Rehabilitation Technology
- Improving mobility solutions through the development of accessible transportation, wheelchair performance assessment, and prosthetic/orthotic optimization to enhance function and independence.
- Integrating biomechanics, human factors, and clinical outcomes research to refine device prescription, enhance usability, and support rehabilitation efforts.
- Education, Training and Knowledge Translation
- Providing continuing education and training for rehabilitation professionals through online courses, symposia, and evidence-based resources to enhance clinical expertise in assistive technology and rehabilitation science.
- Supporting student and professional learning through research mentorship, Capstone projects, and international collaborations to advance knowledge and innovation in the field.
- Health care Policy, Equity and Systems Change
- Using data-driven insights to inform policy and advocacy efforts, ensuring equitable access to assistive technology, mobility solutions, and rehabilitation services for underserved populations.
- Advancing a rights-based approach and systems-thinking perspective to improve personal recovery, social integration, and long-term support for individuals with psychosocial and cognitive disabilities.
- Driving improvements in healthcare coverage, funding models, and service delivery through large-scale data analysis, stakeholder engagement, and systems-level research.
- Supporting national/international efforts to translate assistive technology research into real-world solutions through collaboration with industry partners, grantees, and policymakers.
Active Research Labs and Projects
Assistive Technology Innovation and Commercialization
The Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology focuses on solving user- and clinician-driven challenges by innovating and commercializing assistive technologies (ATs). Projects range from clinical decision support systems to solutions to support older adults as they age in place. In addition to Pitt-led innovations, our team also assists grantees nationwide with AT technology translation via the IMPACT Center, which provides tools and resources to increase the capacity of researchers and entrepreneurs to perform successful Assistive Technology Tech Transfer, and the Healthy Home Laboratory (HHL), a community-based interdisciplinary program that collaborates with companies and researchers to develop scalable solutions to help older adults and individuals with disabilities live safely and independently at home.
- Contact: Jon Pearlman
- Websites:
Product Performance, Standards and Clinical Usability
The Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology focuses on product performance testing, standards development, and clinical usability research to ensure assistive technologies meet high-quality benchmarks. We provide manufacturers with data for product assessment and benchmarking, help consumers and clinicians compare and select products, and support regulators, purchasers, and third-party payers in making informed decisions for policies and reimbursement. Our team maintains a comprehensive library of product performance data collected in accordance with national and international testing standards. We also develop and implement human subject research protocols to evaluate clinical efficacy, human factors, and usability, ensuring that assistive products are both effective and user-friendly.
- Contact: Dave Brienza
- Website: https://www.wheelchairstandards.pitt.edu
Smart Technology for Accessibility, Aging and Independence
The Accessible SmartTech Research Group is committed to transforming smart technology to enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities. From smartphones and wearables to smart home tech and assistive robotics, we innovate and tailor both mainstream and custom solutions while advancing implementation through assessment, training, and policy to improve inclusion. Our work is supported by the Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center on Wireless Technology (Wireless RERC), the SmartTech Hub for Paralysis Care (ST4P) and a number of research grants.
- Contact: Dan Ding
- Website: https://www.smarttech.pitt.edu
The Cognitive Health Across the Life Span Research Group focuses on leveraging smart technology to support healthy brain aging and improve the quality of life for individuals with neurodegenerative conditions. We emphasize human-centered design in both technology development (hardware and software) and rigorous technology evaluation. To ensure our solutions are informed by real-world needs, we actively engage advisory groups and stakeholder participants, including individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) and their caregivers. Their insights help shape our research, ensuring that smart technology is both accessible and impactful in enhancing cognitive health and daily living.
- Contact: Julie Faieta
Mobility, Prosthetics and Rehabilitation Technology
The Inclusive Mobility Research Lab conducts empirical human factors research into methods, measures, and models for accessible and inclusive design of transportation technologies related to public transit, driving, and active transportation modes; associated services; and built environments—with the goal of improving health and mobility in the community. Key areas of focus include engineering anthropometry, functional biomechanics, and analysis of human perception-cognition-movement capabilities in transportation-disadvantaged populations, particularly older adults and individuals with sensory and mobility impairments.
- Contact: Clive D’Souza
- Website: www.includable.org
The Epiphron Prosthetics & Orthotics Research Lab aims to improve prescription, fitting and function of prosthetic and orthotic devices as well as to improve training and education for both users and members of their care team. To that end, we conduct scientific research on prosthetic socket comfort, on orthotic joint technology, and on real-life outcomes of prosthetic and orthotic interventions. We also develop and test innovative approaches to prosthesis fitting optimization, phantom pain treatment, and prosthetic gait retraining. Our lab is closely integrated with our Master of Science in Prosthetics and Orthotics (MSPO) program and facilitates approximately 25 student Capstone research projects along with additional projects by PhD students and undergrad research interns each year.
- Contact: Goeran Fiedler
The Tissue Integrity Management Research Group is dedicated to the prevention, evaluation and treatment of soft tissue pathology. We study the mechanical, biochemical, and physiological factors related to tissue viability and pressure injuries. We develop and evaluate innovative seat cushion technology, support surface technology, and devices for use in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. We are leaders in the development of national and international standards for these devices.
- Contact: Dave Brienza
Education, Training and Knowledge Translation
The Rehabilitation Science & Technology Continuing Education (RSTCE) Program advances post-professional education, training, and knowledge translation in rehabilitation and assistive technology. Through evidence-informed instructional design, it enhances workforce competency and integrates best practices into clinical and community settings. Best known for hosting the International Seating Symposium (ISS), RSTCE also supports global knowledge dissemination. Over the past 15 years, it has expanded into online and on-demand learning, developing grant-funded courses such as ATPrep, EVoTAS, and TWSPO to improve accessibility and scalability. With a network of over 10,000 professionals, RSTCE delivers research-based education through webinars, certificate programs, and professional development courses. Its interdisciplinary team ensures effective knowledge translation, bridging research, education, and practice.
- Contact: Rachel Hibbs
- Website: https://www.shrscontinuingeducation.pitt.edu/programs-department/rehabilitation-science-and-technology
The Capacity Building in Assistive Technology Service and Innovation Group investigates systemic barriers and facilitators in assistive technology service delivery, developing evidence-based strategies to improve adoption, workforce training, and policy implementation. Through regional and global collaborations, we facilitate knowledge exchange among AT providers, innovators, policymakers, and users to optimize service models. Our research explores effective pathways for scaling AT solutions, studying policy development, funding mechanisms, and adoption trends. By integrating implementation science and stakeholder engagement, we contribute to sustainable AT ecosystems that bridge innovation and real-world applications.
- Contact: Mary Goldberg
Health care Policy, Equity and Systems Change
The Advocacy and Data Outcomes in Assistive Mobility (ADOAM) Lab serves to acquire, develop, curate, and analyze large datasets related to custom configured complex wheelchair devices and services in order to report research findings. This research serves to inform equitable, sustainable, and evidence-based practices and coverage policies to improve health, function, and community living for people with disabilities. This work is spearheaded by a collective group of researchers, consumers, clinicians, advocates, industry partners, and policy organizations with a common interest in further demonstrating the effectiveness and benefits of various assisted-mobility devices and associated services. ADOAM projects are typically funded through both government and private sector research grants. The ADOAM Lab welcomes students and trainees to become involved. For the most part, the lab is virtual and, therefore, is a center for collaboration across several clinical and research institutions and organizations. The group has access to several large datasets that have evolved internally within the lab as well as externally. Examples of current projects include the development of new value-based coverage policies for assisted mobility, functional outcomes, analysis of repair and maintenance issues, impact of telehealth, and the application of artificial intelligence to clinical practice and research.
- Contact: Mark Schmeler
- Websites:
The Psychosocial Rehabilitation and Inclusion (PRI) Lab is an international research and education lab committed to research and policy action to support personal recovery and improved social and occupational functioning for individuals with psychosocial and/or cognitive disabilities. In order to achieve this objective, we have adopted a rights-based approach and systems thinking perspective to engage stakeholders and identify systems of support for individuals with psychosocial and/or cognitive disabilities.
- Contact: Ikenna Ebuenyi
Industry Partnerships and Contracted Services
The University of Pittsburgh’s Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology (RST) has successfully collaborated with industry partners and supplied contracted services for more than two decades. A sampling of these partners is listed below. RST is always seeking to expand and enhance the list of external partners we work with. Please reach out to Dave Brienza with any inquiries concerning opportunities in these areas.
RST Industry Partnerships
RST collaborates with industry partners to perform research and development for assistive and rehabilitation products and services—including product design and development, laboratory testing, clinical evaluation, human factors and usability assessments, best practice development, and training programs.
These collaborations can be supported by several mechanisms that most frequently involve either direct payment for services or federal grant dollars awarded through the NIDILRR Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program, which funds research and development for small businesses interested in commercializing new technologies. Funding typically ranges from $150,000 to $1 million, depending on the phase of development and grant specifications. RST’s IMPACT Center offers industry partners the guidance and support needed to pursue these funding streams. Additional information and contact details can be found on the IMPACT webpage.
RST Contracted Services
RST has a rich history of providing product development and evaluation services for manufacturers, suppliers, third-party payers, and foundations. Services include development, laboratory testing, and clinical evaluation of assistive and rehabilitation products.
Examples of products evaluated for performance and durability:
- Wheelchair Testing (ISO 7176 and RESNA WC-1/WC-2)
- Wheelchair Caster Testing (ISO 7176-32)
- Wheelchair Cushion Testing (ISO 16840 and RESNA WC-3)
- Office Chair Testing
- Mattress Testing (RESNA SS-1)
- Operating Room Overlay Testing
- Wheelchair Drive Wheels and Caster Rolling Resistance Testing
Companies/organizations we have worked with:
- Hillrom
- Invacare
- Permobil
- Arjo
- Turncare
- Dabir Surfaces
- ROHO
- VGM/US Rehab
- Wheels for Humanity
- Anthros
- Tamarack
- Game Changer Technologies
- ASP Global
- Rolapal
- Supracor
- USCAR (US Council for Automotive Research)
- Pratt Miller Engineering
Publications
RST has published and presented its research since 1994. For a look at RST’s most recent publications using PubMed, please select the links below:
Research Experiences
We offer students opportunities to engage in research experiences within the Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology. Participation in research will help you gain critical skills and complement classroom learning.
Available options include volunteer as well as paid positions and are available to Pitt students and non-Pitt students. Please fill out the appropriate link below.
Before applying, we encourage you to take a look at RST Research areas, publications and faculty to help get a better idea of what RST Research has to offer.
Student Research Opportunities
Pitt Students (undergraduate, graduate)
If you are a Pitt student interested in exploring research opportunities, please complete the SHRS Student Research Tracker at this link. You MUST have an active Pitt e-mail to complete this form.
- Under the “Disciplines” section, please choose “Rehabilitation Science and Technology” as “Primary Discipline.” This will ensure that your application is routed to RST first.
- If we are unable to provide a position at RST, your application will be routed to any additional departments you indicate under “Disciplines” (Choice 2 and so on).
Non-Pitt Students
If you are not enrolled at Pitt but are interested in exploring research opportunities, please complete the Online Research Interest Form at this link. Your information will be shared with all RST Research faculty and kept on file.
Study Recruitment
The department is recruiting research participants for the following research studies. Please review the studies below for details. If you are interested in learning more, reach out by phone or e-mail to the contact provided for that particular study.
Smart Home Service Delivery
We are evaluating the impact of a smart home technology service designed to help individuals with disabilities choose and be trained on smart home devices and applications that can assist with the tasks and activities of daily living.
- Contact Name: Jessica Boateng (jsb145@pitt.edu)
Technology and Disability Research Registry
The purpose of the Technology and Disability Research (TDR) Registry is to support technology use among persons with disabilities by sharing technology-related research participation opportunities and educational information with persons with disabilities, caregivers, and professionals who provide health or social services to persons with disabilities.
Be sure to check back for additional opportunities!
International Seating Symposium
The International Seating Symposium (ISS) is the world’s largest academic conference in the field of seating, mobility, and assistive technology for people with disabilities. ISS draws key stakeholders from the continuum of care: clinicians, researchers, manufacturers, suppliers, consumers, and more are all present at the events.
Since its inception in 1982, ISS has been hosted annually across North America. The event is expected to draw close to 2,500 participants and roughly 100 exhibitors for a meeting that includes the exhibit hall, plenary sessions, instructional courses, research papers, and posters presentations by experts from around the world.
The ISS team also supports partner conferences in other continents including the European Seating Symposium, Latin American Seating Symposium, and Oceania Seating Symposium.
Learn more about ISS, find registration information, and view the event schedule on the ISS website.
Questions can be directed to the ISS team at rst_ce@pitt.edu.
People

Melissa Aleksak
Director of the Adaptive Driving Program, Assistant Professor
melissa.aleksak@pitt.edu
Helen Cochrane
Director of the Prosthetics and Orthotics Program, Assistant Professor
hec65@pitt.edu
Rory Cooper
Assistant Vice Chancellor for Research for STEM-Health Sciences Collaborations, Distinguished Professor
rcooper@pitt.edu
Rosemarie Cooper
Associate Director of Stakeholder Engagement at HERL, Associate Professor
cooperm@pitt.eduCommunity Engagement
Training Programs:
- Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology Continuing Education (RSTCE)
- Innovation Institute
- Institute for Clinical Research Education
- International Seating Symposium (ISS)
- International Society of Wheelchair Professionals
Service
The Center for Assistive Technology (CAT) provides comprehensive services to its clients based on their needs and personal goals. A joint program of UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh, CAT has emerged as a leader and innovator in the assistive technology field. RST students have opportunities for experiential learning with AT leaders through the center.
Resources
Current Student Hub
Students can find access to program and school materials in the Current Student Resource Hub. Pitt Passport is required.
Current Students can also find answers to commonly asked questions and connect with valuable resources and contacts. This resource helps students locate academic guidance, professional development, or support for each individual’s wellbeing including things like counseling or study resources.

























































